Earth is trapping twice, as
much heat, as of 2005, now at an unprecedented pace ?
Earth is trapping twice, as
much heat, as of 2005, now at an unprecedented pace ?

Dr Srikanta K. Panigrahi
Director General and
Distinguished Research Fellow, IISD
Indian Policy Maker and Technocrat
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), USA warned
that the Earth is trapping twice as much heat as in 2005, now at an unprecedented pace ?
Researchers from NASA have warned the Earth is trapping heat at a rate so much higher, it's "unprecedented." The amount of heat
being trapped by Earth has roughly doubled since 2005, the study found. The NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)
study pointed to human activities and changes in the oceans to be responsible as the key reasons.
They found in a new study released recently in June, 2021, that Earth's "energy imbalance approximately
doubled during the 14-year period from 2005 to 2019." The energy imbalance is simply how much heat
the Earth absorbs from the sun, compared to how much "thermal infrared radiation" the Earth radiates back into space.
Norman Loeb, the study's Lead Author and a NASA Investigator, said: "The magnitude of this increase is not to be taken lightly as it is unprecedented." Researchers pointed to human activities as one of the main reasons for the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) generation. The study said the Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) from human activities were trapping heat in the atmosphere that then melted snow and ice, which in turn put more water vapour into the atmosphere, thereby preventing radiation from escaping. It also said that a "naturally occurring" shift in the Pacific Ocean from a cool phase to a warmer one is likely to have played a big role, to be witnessed so far.
The researchers used a series of satellites and a network of ocean floats to reach their findings, and compared the data from each. The Cover reflects One Of Such Satellite images of the tapped heat.
Norman Loeb again viewed: "The two very independent ways of looking at changes in Earth's energy imbalance are in really, good agreement, and they're both showing this very large trend, which gives us a lot of confidence that what we're seeing is a real phenomenon and not just an instrumental arti-fact. "The trends we found were quite alarming in a sense."
How Antarctica hit record temperature ?
From Canada to Russia, temperatures have been soaring with the attendant threat to flora and fauna sparking concern among experts and the public alike. And, now, the astounding reports of record-breaking heat waves in some of the coldest places on the planet, is coming, like that Antarctica, too, has registered a new high of heating, hence resulting in melting ice caps at a rapid pace, that had never happened before.
The World Meteorological Organisation (WMO), a United Nations body, announced on 1 July, 2021 that the new record for the maximum temperature for the southernmost continent is now 18.3 degrees Celsius, eclipsing the previous high of 17.5 degrees Celsius in March 2015.
The reading that revealed the latest high was taken in February 2020, at the same ice station, called Esperanza
and run by Argentina, where the previous high was recorded. Interestingly, or perhaps alarmingly you might say,
there was an even higher reading for Antarctica of 20.75 degrees Celsius recorded by a Brazilian station, again,
in February 2020 that was actually shot down by a WMO review team because of issues with the measurement device.
It has to be kept in mind that the new record is only for the continent of Antarctica. The highest the mercury has ever gone for the larger Antarctic region, which comprises Antarctica and all ice or land south of 60 degrees latitude, is 19.8 degrees Celsius, recorded in January 1982.
Why it is a cause for worry ?
The year 2020 was the hottest on record globally after 2016, with the decade of the 2010s now classified as being the
hottest decade ever since scientists started measuring the weather. Experts say it is undoubtedly human-induced climate change at
work behind such rise in temperatures. The Antarctica region has been termed one of the "Earth's final frontiers" and, along with the Arctic, is seen as playing "an important role in driving climate and ocean patterns and in sea level rise".
Experts said that the Antarctic Peninsula, which is the northernmost tip of the continent, lying closest to South America, "is among the fastest warming regions of the planet, almost three degrees Celsius over the last 50 years".
"This new temperature record is, therefore, consistent with the climate change we are observing," said WMO Secretary-General Professor Petteri Taalas. The WMO again said that the continent of Antarctica is roughly twice the size of Australia and stretches across a total of 14 million square kilometres. Characterised by a cold, windy and dry climate, Antarctica sees average annual temperatures that range between -10 degrees Celsius at the coast to -60 degrees Celsius in the most elevated parts in the continent's interior.
WMO adds that its "immense ice sheet is up to 4.8km thick and contains 90 per cent of the world's fresh water, enough to raise sea level by around 60 metres were it all to melt".
What caused the record reading ?
The specific factor that drove up the temperature in Antarctica was, the WMO said, a large high-pressure system that created "down slope winds producing significant surface warming", and conditions that it added were "conducive for producing record temperature scenarios".
However, for the underlying cause, one may not need to look further than climate change. "This new record shows once again that climate change requires urgent measures. It is essential to continue strengthening the observing, forecasting and early warning systems to respond to the extreme events that take place more and more often due to Global Warming," said Argentine expert and First Vice President of WMO, Professor Celeste Saulo.
Referring to the heat waves in the northern hemisphere those have seen records been broken across Russia, Eastern Europe, the US and Canada, WMO said that "the heat is more typical of summer temperatures in West Asia" than areas that are home to glaciers, which means "there is a consequent risk of high glacier melt".
Climate change poses risks to "Health, Livelihoods, Food Security, Water Supply, Human Security, and
Economic Growth", which can be exacerbated with Global Warming of 1.5 degrees Celsius over pre-industrial
levels. Limiting warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius, rather than 2 degrees Celsius, "could result in 420 million
fewer people being exposed to severe heat waves", the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has said.
The Author is a Leading Indian Sustainability Thought Leader and Director General at Indian Institute of Sustainable Development (IISD), New Delhi and deeply engaged in Climate Action Leadership Initiatives of UNFCCC, UNEP and Government of India. Dr Panigrahi is a National Science Popularization Award Winner, 2004-05.

Image of the Sun taken by Extreme Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (EIT) of the NASA and ESA-operated The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) aircraft.
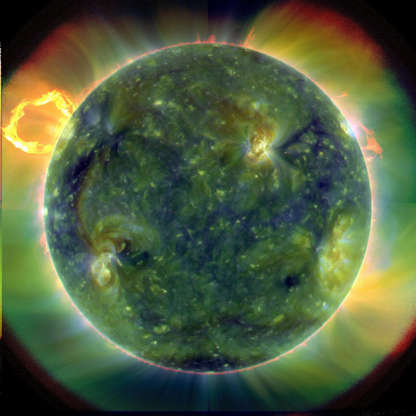
Am extreme ultraviolet image of the Sun taken by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO).

Am extreme ultraviolet image of the Sun taken by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO).
Melting of Antarctica Ice Caps

© Posnov/Getty Sailing through enormously huge icebergs near Melchior islands in Antarctica.
The scorching temperatures from the West US's third heat wave of this summer, which fueled quick-spreading wildfires
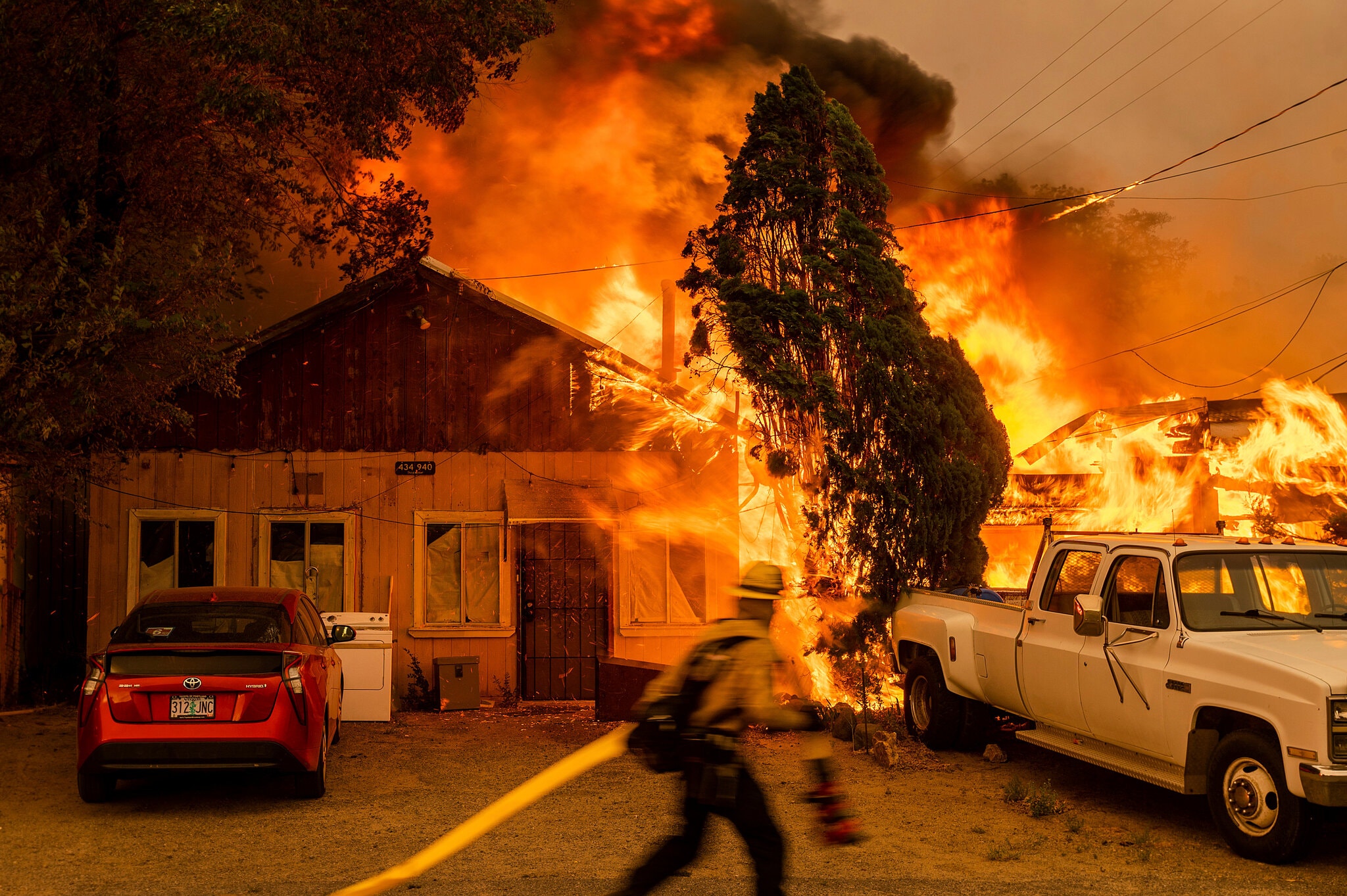

A wildfire consumed a home in Doyle, Calif., on Saturday.
Pushed by heavy winds, the Sugar Fire, part of the Beckwourth Complex,
came out of the hills and destroyed several homes.
Phoro Credit | Noah Berger/Associated Press
Source: The New York Times | 13th July 2021
IMD says severe heatwave to continue for next 4-5 days in this part of India

A rickshaw puller covers his face from the heatwave as temperature gets near 44 degrees in New Delhi.
Source: LiveMint | 01st July 2021










